As we embark on a new year, I am energized by the transformative potential of artificial intelligence and cloud computing in healthcare. These technologies are poised to redefine the industry, possibly more profoundly than anything we have witnessed in the past century. Crucially, the hope for these new technologies is how they will enable improved access to healthcare for the 4.5 billion people worldwide who currently lack essential health services.
Throughout my career, I’ve had the privilege of leading initiatives at organizations like the FDA and Amazon. I continue to remain inspired by the impact of initiatives like the precisionFDA platform, which launched nearly a decade ago, and continues to deliver far-reaching impacts in diverse fields like oncology, liquid biopsies, and rare disease diagnostics.
Today, at GE HealthCare, I am excited to see how we are leveraging state-of-the-art AI and cloud computing to accelerate the development of groundbreaking technologies. We are working to deliver the next generation of AI-enabled devices because we want to make them smarter and more accessible. We have new innovations in development that will help reduce cognitive overload for physicians and improve operational efficiencies in hospitals, ultimately with the goal of delivering better experiences and outcomes for patients.
Here are seven key observations from the broader healthcare landscape along with innovations from GE HealthCare that outline how the possibilities opened up by these technologies can help transform the future of healthcare.
1. AI adoption in healthcare remains slow despite the explosion of data
According to Statista, by 2025, the world is expected to generate more than 180 zettabytes of data, with more than one-third projected to originate from healthcare. Yet only half of the healthcare industry is estimated to adopt cloud services to manage this data effectively. The healthcare sector's hesitation in embracing AI contrasts with industries like music and e-commerce, where AI has proven effective in making sense of large datasets.
Source: Statista 2024
2. Multimodal data and custom AI models pose challenges
Most of the healthcare industry’s multimodal data (e.g., medical images, notes, audio recordings, device readings) is unstructured, making it difficult for traditional analytics and most machine learning algorithms to process.
Additionally, traditional machine learning approaches require vast amounts of domain-specific data and manual feature engineering for different disease states, leading to costly and resource-intensive AI model development cycles—further underscoring why current approaches are not sustainable.
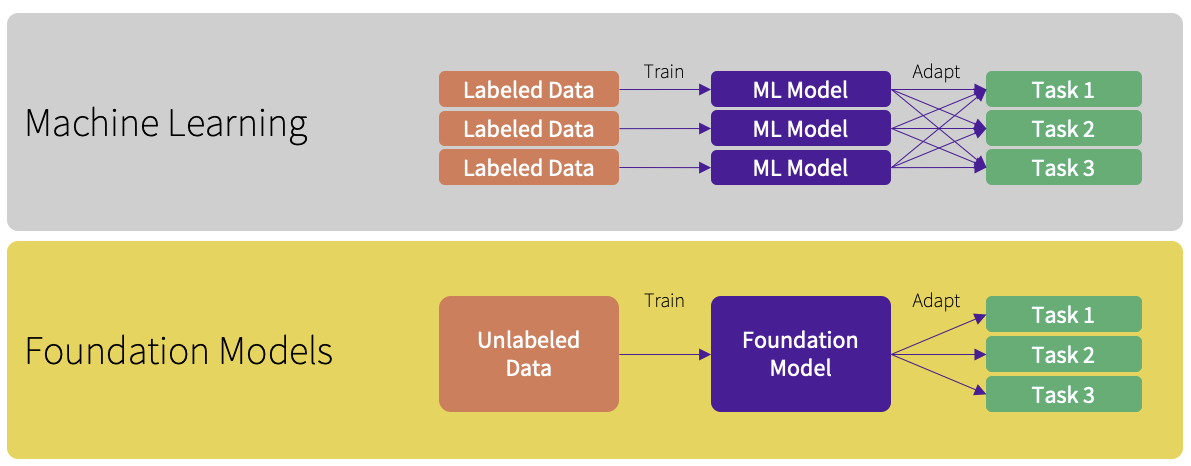
3. Foundation models offer a scalable solution
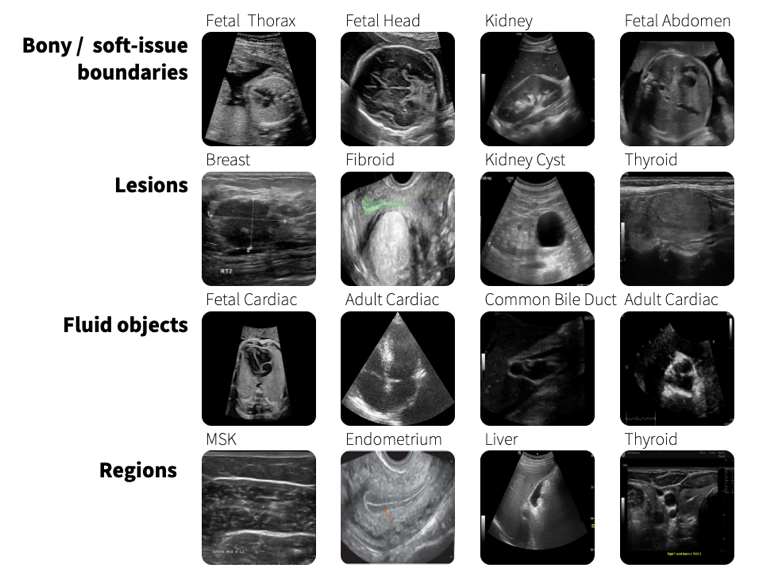
Foundation models can help mitigate the challenges presented by the need for constant customization of AI models. These models can be trained on a broad range of multimodal data enabling them to be applied across different healthcare tasks without extensive retraining. GE HealthCare has been pioneering the development of purpose-built foundation models in healthcare. To give one example, SonoSAMTrack[1] is a foundation model in the research stage that offers a tool for interactive segmentation of objects of interest on ultrasound images and scans. It is designed to adapt to new data and tasks without requiring extensive retraining.
In addition, the GE HealthCare research and development team has built the industry’s first full-body X-ray foundation and 3D MRI model[2]. Even though our model is a full-body foundation model – in our internal testing, it outperforms even more specialized models.
Read now: Introducing a Multimodal AI HealthCare Model Trained on Comprehensive New Dataset
Read now: GE HealthCare Unveils Research on Advanced 3D MRI Foundation Model
4. Clinicians face cognitive overload and workflow inefficiencies
According to the World Health Organization, by 2050, the global population of people 60 and older is expected to double, to 2.1 billion. As the global population increases, so does the exponential growth of data, spanning industries such as clinical data, electronic health records, medical imaging, genomics, ingestibles and implantables, wearables and sensors.
In addition to the explosion of data, clinicians struggle with workflow inefficiencies. Managing vast amounts of information manually from numerous sources can lead to delays, errors, and burnout. Providing adequate resources and access to care is essential, but orchestrating the necessary coordination and workflows across numerous touchpoints and overwhelming data is challenging. This complexity contributes to delays in care, medical errors, and clinician burnout. According to a 2024 retention and staffing report from Nursing Solutions Inc., nearly half of clinicians report high levels of burnout, and hospitals average a 100% staff turnover approximately every five years.
5. CareIntellect can enhance the patient care journey and workflow efficiencies
GE HealthCare is developing CareIntellect, a new cloud-first offering designed to optimize care delivery across various disease states and health networks - from screening to detection, treatment planning, and monitoring of treatment response. Applications in development to be offered as part of CareIntellect are focused on both clinical and operational use cases.
Once a customer installs their first CareIntellect application, they would be able to activate additional applications (which will become available in the future) quickly, securely, and without costly integration. All applications will leverage a common data layer and integrate with a provider’s single sign-on application, enabling clinicians to focus on their patients. GE HealthCare is developing multiple applications in the CareIntellect offering, focusing on both clinical and operational use cases. Our first application is CareIntellect for Oncology that is designed for oncologists and care teams. The application aggregates and summarizes multimodal patient data from disparate systems, using generative AI to summarize patient notes and reports. Additionally, CareIntellect for Oncology helps care teams assess potentially suitable clinical trials by comparing the patient’s health record to trial eligibility criteria.
Learn more about CareIntellect for Oncology
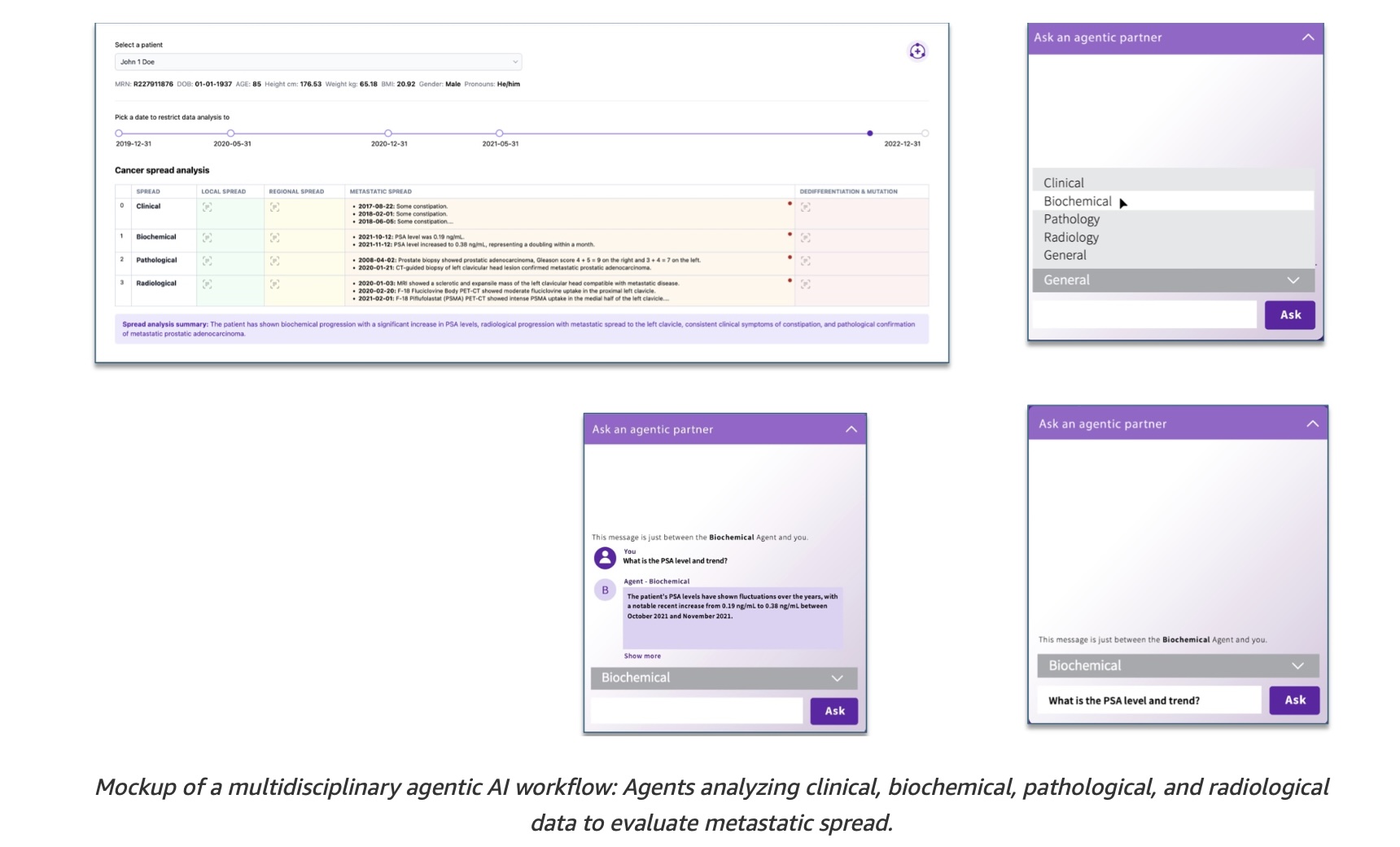
6. Project Health Companion aims to harness the potential of agentic AI
The Health Companion project, currently in research, represents a new era in AI: a shift from models generating text, images, and video or answering questions to agents that can interact with their environment and act to accomplish predefined goals.
The Health Companion project explores whether an agentic AI approach driven by multiple agents – each trained in a particular area (e.g., genomics, radiology, pathology, etc.) - could help clinicians bring clarity to their thinking while interacting with these agents, therefore streamlining their clinical decision-making to deliver more personalized care.
Read more: How agentic AI systems can solve the three most pressing problems in healthcare today
7. Using AI to forge the path to more equitable healthcare
AI has the potential to bridge healthcare disparities and help enable access to quality care for the 4.5 billion[3] people in the world currently uncovered by essential services.
One example of GE HealthCare's focus on accessibility is Vscan Air. Vscan Air is a portable ultrasound device that enables patients to receive quality imaging wherever they are located. Powered by Caption AI software, the device provides real-time guidance to practitioners that are not experts in ultrasound imaging, allowing even those without extensive training to capture diagnostic-quality ultrasound images.
Every breakthrough in AI for healthcare promises quality care for everyone. The future relies on collaboration between human expertise and artificial intelligence to transform possibilities into reality.
References
[1] Technology in development that represents ongoing research and development efforts. These technologies are not products and may never become products. Not for sale. Any reported results are preliminary and subject to change. Not cleared or approved by the U.S. FDA or any other global regulator for commercial availability.
[2] Concept only. This work is in concept phase and may never become a product. Not for Sale. Any reported results are preliminary and subject to change. Not cleared or approved by the U.S. FDA or any other global regulator for commercial availability.
[3] Source: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/universalhealthcoverage